Solar inverters serve as the brain and nervous system for photovoltaic systems, maintaining and regulating the conversion of direct current electricity into alternating current. Without a properly functioning inverter, a solar panel installation would be rendered nonfunctional. While the diverse inverter options available on the market today may seem daunting to navigate, a bit of research combined with foundational knowledge can empower homeowners to make informed decisions about the inverter type best suited to their needs. To assist in this important selection process, we have delineated the distinguishing characteristics between three predominant inverter varieties: on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid inverters. Grasping the contrasts between these three systems is pivotal for identifying the optimal solar solution for one's home.
On-Grid Inverters
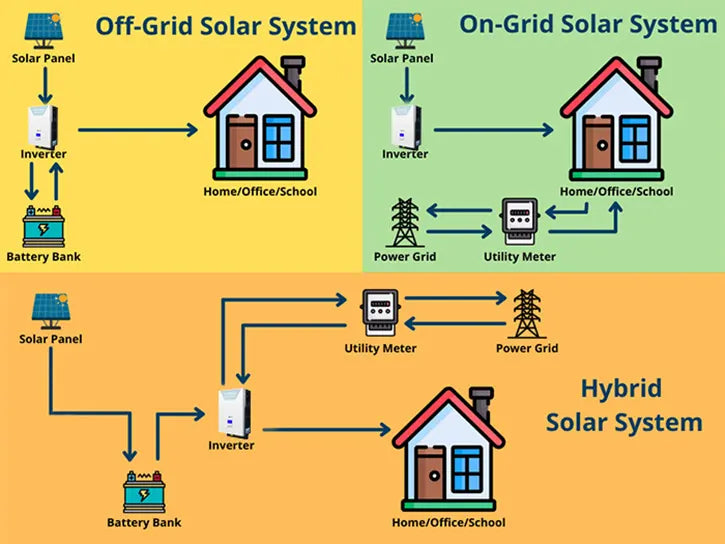
On-grid inverters are also known as grid-tied inverters. These types of inverters are designed to work in conjunction with the utility power grid. An on-grid inverter converts the DC electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which can be used to power appliances and devices in your home or business. The excess electricity that is generated by the solar panels is fed back into the utility power grid, and your utility company will credit your account for the excess electricity that you generate.
On-grid inverters are the most common type of inverter used in residential and commercial solar power systems. They are less expensive than off-grid and hybrid inverters because they do not require batteries or additional equipment to store excess electricity. However, on-grid inverters do not provide backup power in the event of a power outage. When the utility power grid goes down, your solar power system will also be shut down for safety reasons.
Off-Grid Inverters
Off-grid inverters, also known as standalone inverters, are designed to work independently of the utility power grid. These types of inverters are used in remote locations where there is no access to the utility power grid. Off-grid inverters convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity, which can be used to power appliances and devices in your home or business.
Since off-grid inverters are not connected to the utility power grid, they require batteries or other energy storage systems to store excess electricity. These batteries can be expensive and require regular maintenance. However, off-grid inverters provide backup power in the event of a power outage. When the utility power grid goes down, your solar power system will continue to function, providing you with electricity until power is restored.
Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters, also known as grid-interactive inverters, are a combination of on-grid and off-grid inverters. These types of inverters can operate in both on-grid and off-grid modes, depending on the situation. Hybrid inverters are designed to work with the utility power grid, but they also have the capability to store excess electricity in batteries for backup power.
When the utility power grid is up and running, the hybrid inverter will convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity, which can be used to power appliances and devices in your home or business. The excess electricity is fed back into the utility power grid, and you will be credited for the excess electricity that you generate. When the utility power grid goes down, the hybrid inverter will switch to off-grid mode and provide backup power from the batteries.
Hybrid inverters are more expensive than on-grid inverters but less expensive than off-grid inverters. They provide the best of both worlds by allowing you to generate and store your own electricity while also being connected to the utility power grid. This means you can enjoy the benefits of solar power while also having access to backup power in the event of a power outage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the type of inverter you choose for your solar power system depends on your unique situation. If you live in a remote location with no access to the utility power grid, an off-grid inverter may be your only option. If you are connected to the utility power grid and want to save money on your electricity bill, an on-grid inverter may be the best choice for you. If you want the benefits of both on-grid and off-grid inverters, a hybrid inverter may be the way to go.
When choosing an inverter, it is important to consider your current and future energy needs, as well as your budget. You should also consult with a professional installer to ensure that you choose the right type and size of inverter for your specific solar power system. With the right inverter, you can enjoy the benefits of solar power, reduce your carbon footprint, and save money on your electricity bill.